JavaScript 项目中 CockroachDB 的内省
使用 Prisma ORM 内省你的数据库
在本指南中,我们将使用一个包含三个表的演示 SQL schema
CREATE TABLE "User" (
id INT8 PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT unique_rowid(),
name STRING(255),
email STRING(255) UNIQUE NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE "Post" (
id INT8 PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT unique_rowid(),
title STRING(255) UNIQUE NOT NULL,
"createdAt" TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT now(),
content STRING,
published BOOLEAN NOT NULL DEFAULT false,
"authorId" INT8 NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY ("authorId") REFERENCES "User"(id)
);
CREATE TABLE "Profile" (
id INT8 PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT unique_rowid(),
bio STRING,
"userId" INT8 UNIQUE NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY ("userId") REFERENCES "User"(id)
);
注意:某些字段用双引号括起来,以确保 CockroachDB 使用正确的字母大小写。如果未使用双引号,CockroachDB 会将所有内容读取为小写字符。
展开查看表的图形概览
用户
| 列名 | 类型 | 主键 | 外键 | 必需 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
id | INT8 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 自动递增 |
name | STRING(255) | 否 | 否 | 否 | - |
email | STRING(255) | 否 | 否 | 是 | - |
帖子
| 列名 | 类型 | 主键 | 外键 | 必需 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
id | INT8 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 自动递增 |
createdAt | TIMESTAMP | 否 | 否 | 是 | now() |
title | STRING(255) | 否 | 否 | 是 | - |
content | STRING | 否 | 否 | 否 | - |
published | BOOLEAN | 否 | 否 | 是 | false |
authorId | INT8 | 否 | 是 | 是 | - |
个人资料
| 列名 | 类型 | 主键 | 外键 | 必需 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
id | INT8 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 自动递增 |
bio | STRING | 否 | 否 | 否 | - |
userId | INT8 | 否 | 是 | 是 | - |
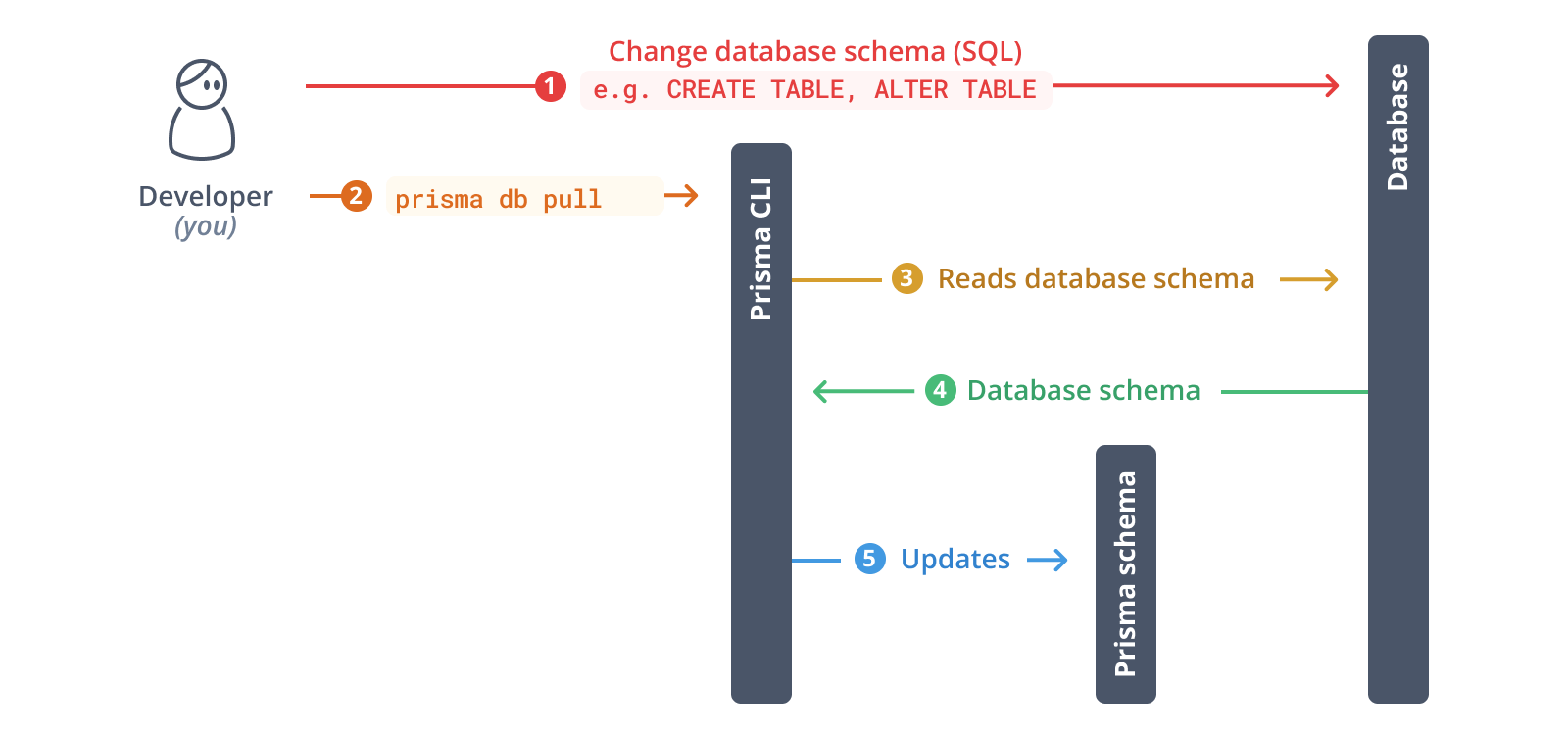
接下来,你将内省你的数据库。内省的结果将是你的 Prisma schema 中的一个数据模型。
运行以下命令来内省你的数据库
npx prisma db pull
此命令读取用于在 schema.prisma 中定义 url 的环境变量 DATABASE_URL(在我们的例子中,它设置在 .env 文件中),并连接到你的数据库。一旦连接建立,它将内省数据库(即*读取数据库 schema*)。然后,它将数据库 schema 从 SQL 转换为 Prisma 数据模型。
内省完成后,你的 Prisma schema 将被更新
数据模型现在看起来类似于这样
model Post {
id BigInt @id @default(autoincrement())
title String @unique @db.String(255)
createdAt DateTime @default(now()) @db.Timestamp(6)
content String?
published Boolean @default(false)
authorId BigInt
User User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id], onDelete: NoAction, onUpdate: NoAction)
}
model Profile {
id BigInt @id @default(autoincrement())
bio String?
userId BigInt @unique
User User @relation(fields: [userId], references: [id], onDelete: NoAction, onUpdate: NoAction)
}
model User {
id BigInt @id @default(autoincrement())
name String? @db.String(255)
email String @unique @db.String(255)
Post Post[]
Profile Profile?
}
Prisma ORM 的数据模型是你数据库 schema 的声明性表示,它作为生成的 Prisma Client 库的基础。你的 Prisma Client 实例将公开*根据*这些模型*定制*的查询。
目前,数据模型存在一些小的“问题”
User关系字段是大写的,因此不符合 Prisma 的命名约定。为了表达更多的“语义”,如果这个字段命名为author,以更好地*描述*User和Post之间的关系,那会更好。User上的Post和Profile关系字段,以及Profile上的User关系字段都是大写的。为了遵循 Prisma 的命名约定,这两个字段都应该小写为post、profile和user。- 即使小写后,
User上的post字段仍然略有命名不当。那是因为它实际上指的是一个帖子列表——因此更好的名称应该是复数形式:posts。
这些更改与生成的 Prisma Client API 相关,在其中使用小写关系字段 author、posts、profile 和 user 会让 JavaScript/TypeScript 开发者感觉更自然和符合习惯。因此,你可以配置你的 Prisma Client API。
因为关系字段是*虚拟的*(即它们*不直接体现在数据库中*),所以你可以在不修改数据库的情况下手动在 Prisma schema 中重命名它们
model Post {
id BigInt @id @default(autoincrement())
title String @unique @db.String(255)
createdAt DateTime @default(now()) @db.Timestamp(6)
content String?
published Boolean @default(false)
authorId BigInt
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id], onDelete: NoAction, onUpdate: NoAction)
}
model Profile {
id BigInt @id @default(autoincrement())
bio String?
userId BigInt @unique
user User @relation(fields: [userId], references: [id], onDelete: NoAction, onUpdate: NoAction)
}
model User {
id BigInt @id @default(autoincrement())
name String? @db.String(255)
email String @unique @db.String(255)
posts Post[]
profile Profile?
}
在这个例子中,数据库 schema 确实遵循了 Prisma ORM 模型的命名约定(只有内省生成的虚拟关系字段不符合约定,需要调整)。这优化了生成的 Prisma Client API 的人体工程学。
使用自定义模型和字段名称
不过,有时你可能希望对在 Prisma Client API 中公开的列和表的名称进行额外更改。一个常见的例子是将数据库 schema 中常用的 snake_case 命名法转换为 PascalCase 和 camelCase 命名法,这对于 JavaScript/TypeScript 开发者来说更自然。
假设你从内省中获得了以下基于 snake_case 命名法的模型
model my_user {
user_id Int @id @default(sequence())
first_name String?
last_name String @unique
}
如果你为此模型生成 Prisma Client API,它将在其 API 中沿用 snake_case 命名法
const user = await prisma.my_user.create({
data: {
first_name: 'Alice',
last_name: 'Smith',
},
})
如果你不想在 Prisma Client API 中使用数据库中的表和列名,你可以使用 @map 和 @@map 来配置它们
model MyUser {
userId Int @id @default(sequence()) @map("user_id")
firstName String? @map("first_name")
lastName String @unique @map("last_name")
@@map("my_user")
}
通过这种方法,你可以随意命名你的模型及其字段,并使用 @map(用于字段名)和 @@map(用于模型名)指向底层表和列。你的 Prisma Client API 现在如下所示
const user = await prisma.myUser.create({
data: {
firstName: 'Alice',
lastName: 'Smith',
},
})
在配置你的 Prisma Client API 页面了解更多信息。