关系
关系是 Prisma schema 中两个模型之间的*连接*。例如,User 和 Post 之间存在一对多关系,因为一个用户可以拥有多篇博客文章。
以下 Prisma schema 定义了 User 和 Post 模型之间的一对多关系。定义关系所涉及的字段已突出显示
- 关系型数据库
- MongoDB
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
posts Post[]
}
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
title String
}
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
posts Post[]
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
title String
}
在 Prisma ORM 层面,User / Post 关系由以下部分组成:
- 两个关系字段:
author和posts。关系字段在 Prisma ORM 层面定义模型之间的连接,并且**不存在于数据库中**。这些字段用于生成 Prisma Client。 - 标量
authorId字段,它由@relation属性引用。此字段**存在于数据库中**——它是连接Post和User的外键。
在 Prisma ORM 层面,两个模型之间的连接**总是**通过关系**两端**的关系字段来表示。
数据库中的关系
关系型数据库
以下实体关系图定义了**关系型数据库**中 User 和 Post 表之间相同的一对多关系
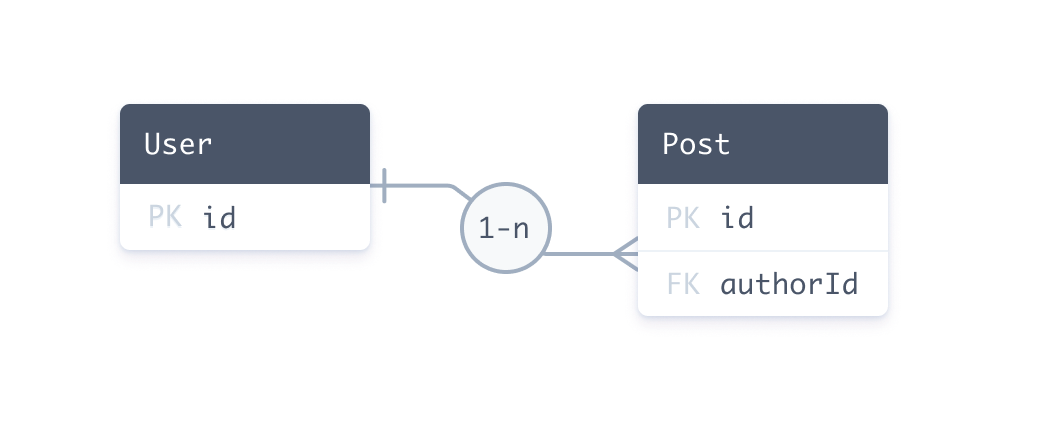
在 SQL 中,您使用*外键*在两个表之间创建关系。外键存储在关系**一侧**。我们的示例由以下部分组成:
Post表中名为authorId的外键列。User表中名为id的主键列。Post表中的authorId列引用User表中的id列。
在 Prisma schema 中,外键/主键关系由 author 字段上的 @relation 属性表示
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
注意:Prisma schema 中的关系表示数据库中表之间存在的关联。如果关系不存在于数据库中,则它也不存在于 Prisma schema 中。
MongoDB
对于 MongoDB,Prisma ORM 当前使用规范化数据模型设计,这意味着文档之间通过 ID 互相引用,方式与关系型数据库类似。
以下文档表示一个 User(在 User 集合中)
{ "_id": { "$oid": "60d5922d00581b8f0062e3a8" }, "name": "Ella" }
以下 Post 文档列表(在 Post 集合中)中的每个文档都有一个 authorId 字段,该字段引用同一个用户
[
{
"_id": { "$oid": "60d5922e00581b8f0062e3a9" },
"title": "How to make sushi",
"authorId": { "$oid": "60d5922d00581b8f0062e3a8" }
},
{
"_id": { "$oid": "60d5922e00581b8f0062e3aa" },
"title": "How to re-install Windows",
"authorId": { "$oid": "60d5922d00581b8f0062e3a8" }
}
]
此数据结构表示一对多关系,因为多个 Post 文档引用同一个 User 文档。
ID 和关系标量字段上的 @db.ObjectId
如果模型的 ID 是 ObjectId(由 String 字段表示),则必须将 @db.ObjectId 添加到模型的 ID 以及关系另一侧的关系标量字段。
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
posts Post[]
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
title String
}
Prisma Client 中的关系
Prisma Client 是从 Prisma schema 生成的。以下示例演示了当您使用 Prisma Client 获取、创建和更新记录时,关系如何体现。
创建记录和嵌套记录
以下查询创建了一个 User 记录和两个连接的 Post 记录
const userAndPosts = await prisma.user.create({
data: {
posts: {
create: [
{ title: 'Prisma Day 2020' }, // Populates authorId with user's id
{ title: 'How to write a Prisma schema' }, // Populates authorId with user's id
],
},
},
})
在底层数据库中,此查询
- 创建一个具有自动生成
id(例如,20)的User - 创建两个新的
Post记录,并将两个记录的authorId设置为20
检索记录并包含相关记录
以下查询通过 id 检索 User,并包含任何相关的 Post 记录
const getAuthor = await prisma.user.findUnique({
where: {
id: "20",
},
include: {
posts: true, // All posts where authorId == 20
},
});
在底层数据库中,此查询
- 检索
id为20的User记录 - 检索所有
authorId为20的Post记录
将现有记录与另一个现有记录关联
以下查询将现有 Post 记录与现有 User 记录关联
const updateAuthor = await prisma.user.update({
where: {
id: 20,
},
data: {
posts: {
connect: {
id: 4,
},
},
},
})
在底层数据库中,此查询使用嵌套的 connect 查询将 id 为 4 的帖子链接到 id 为 20 的用户。该查询通过以下步骤完成此操作:
- 查询首先查找
id为20的用户。 - 然后,查询将
authorID外键设置为20。这将id为4的帖子链接到id为20的用户。
在此查询中,authorID 的当前值无关紧要。无论其当前值如何,查询都会将 authorID 更改为 20。
关系类型
Prisma ORM 中有三种不同类型(或基数)的关系:
以下 Prisma schema 包含每种类型的关系
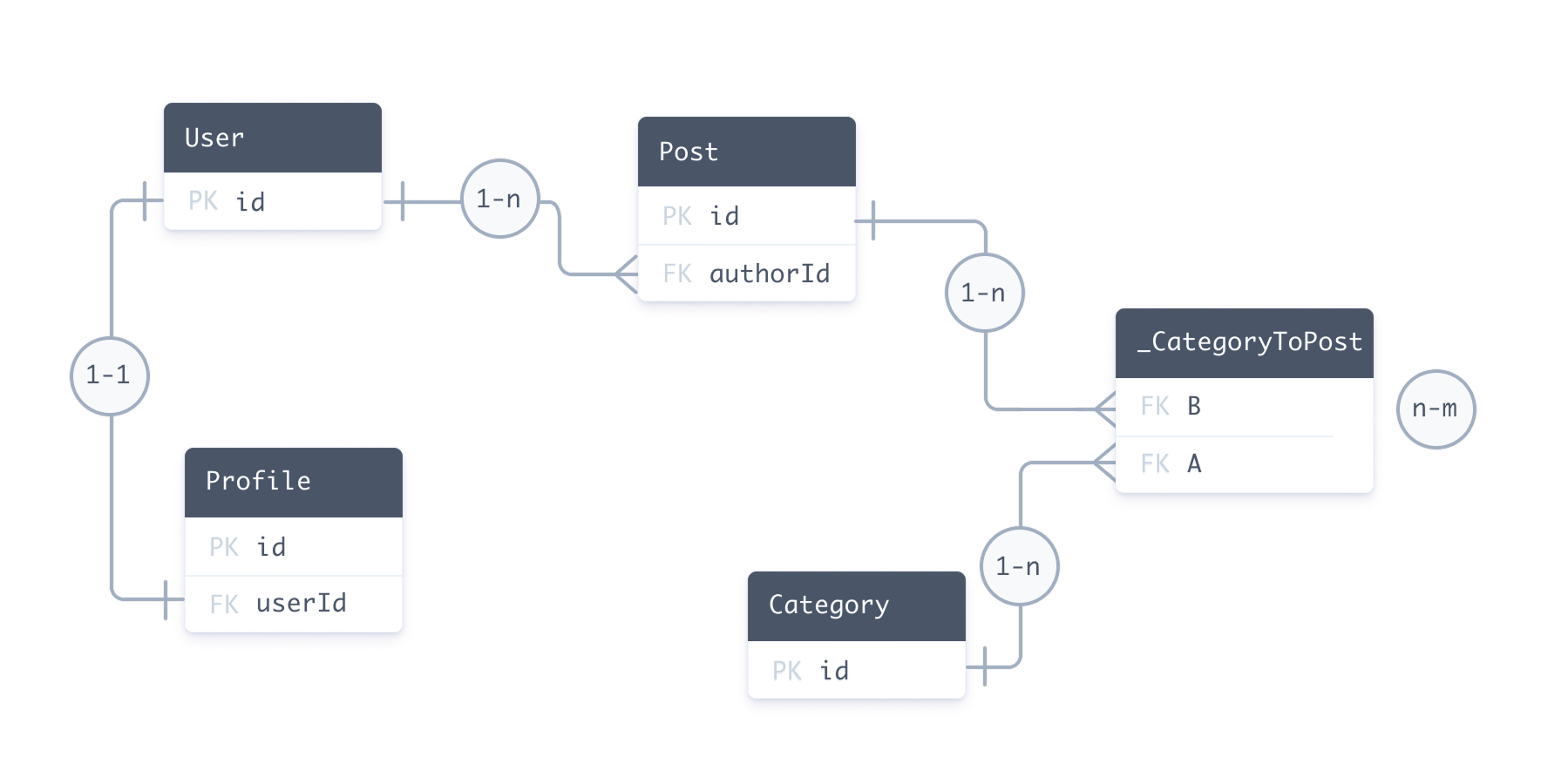
- 一对一:
User↔Profile - 一对多:
User↔Post - 多对多:
Post↔Category
- 关系型数据库
- MongoDB
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
posts Post[]
profile Profile?
}
model Profile {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
user User @relation(fields: [userId], references: [id])
userId Int @unique // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
}
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
categories Category[]
}
model Category {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
posts Post[]
}
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
posts Post[]
profile Profile?
}
model Profile {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
user User @relation(fields: [userId], references: [id])
userId String @unique @db.ObjectId // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
categories Category[] @relation(fields: [categoryIds], references: [id])
categoryIds String[] @db.ObjectId
}
model Category {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
posts Post[] @relation(fields: [postIds], references: [id])
postIds String[] @db.ObjectId
}
请注意,关系型数据库和 MongoDB 之间的语法略有不同——特别是对于多对多关系。
对于关系型数据库,以下实体关系图表示与示例 Prisma schema 对应的数据库
对于 MongoDB,Prisma ORM 使用规范化数据模型设计,这意味着文档之间通过 ID 互相引用,方式与关系型数据库类似。有关更多详细信息,请参阅MongoDB 部分。
隐式和显式多对多关系
关系型数据库中的多对多关系可以通过两种方式建模
隐式多对多关系要求两个模型都具有单个 @id。请注意以下事项:
- 您不能使用多字段 ID
- 您不能使用
@unique代替@id
要使用这些功能中的任何一个,您必须设置显式多对多关系。
隐式多对多关系仍然在底层数据库中体现为关系表。但是,Prisma ORM 管理此关系表。
如果您使用隐式多对多关系而不是显式关系,它会使Prisma Client API 更简单(例如,您在嵌套写入中的嵌套级别会减少一级)。
如果您不使用 Prisma Migrate,而是从内省获取数据模型,您仍然可以遵循 Prisma ORM 的关系表约定来使用隐式多对多关系。
关系字段
关系字段是 Prisma 模型上的字段,其类型*不是* 标量类型。相反,它们的类型是另一个模型。
每个关系必须正好有两个关系字段,每个模型上一个。在一对一和一对多关系的情况下,需要一个额外的*关系标量字段*,它通过 @relation 属性中的两个关系字段之一进行链接。此关系标量字段是底层数据库中*外键*的直接表示。
- 关系型数据库
- MongoDB
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String @unique
role Role @default(USER)
posts Post[] // relation field (defined only at the Prisma ORM level)
}
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
title String
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id]) // relation field (uses the relation scalar field `authorId` below)
authorId Int // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
}
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
email String @unique
role Role @default(USER)
posts Post[] // relation field (defined only at the Prisma ORM level)
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
title String
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id]) // relation field (uses the relation scalar field `authorId` below)
authorId String @db.ObjectId // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
}
posts 和 author 都是关系字段,因为它们的类型不是标量类型,而是其他模型。
另请注意,带注解的关系字段 author 需要在 @relation 属性中链接 Post 模型上的关系标量字段 authorId。关系标量字段表示底层数据库中的外键。
两个关系字段(即 posts 和 author)都纯粹在 Prisma ORM 层面定义,它们不会在数据库中体现。
带注解的关系字段
需要关系的一侧用 @relation 属性*注解*的关系被称为*带注解的关系字段*。这包括:
- 一对一关系
- 一对多关系
- 仅适用于 MongoDB 的多对多关系
用 @relation 属性注解的关系侧表示**在底层数据库中存储外键**的一侧。代表外键的“实际”字段在该关系侧也需要,它被称为*关系标量字段*,并在 @relation 属性内部被引用。
- 关系型数据库
- MongoDB
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId
当标量字段在 @relation 属性的 fields 中使用时,它*成为*关系标量字段。
关系标量字段
关系标量字段命名约定
因为关系标量字段始终*属于*一个关系字段,所以以下命名约定很常见:
- 关系字段:
author - 关系标量字段:
authorId(关系字段名 +Id)
@relation 属性
@relation 属性只能应用于关系字段,不能应用于标量字段。
在以下情况下需要 @relation 属性:
- 您定义一对一或一对多关系时,它在关系的*一侧*是必需的(带有相应的关系标量字段)
- 您需要消除关系歧义时(例如,当两个模型之间存在两个关系时)
- 您定义自关系时
- 您定义适用于 MongoDB 的多对多关系时
- 您需要控制关系表在底层数据库中的表示方式时(例如,为关系表使用特定名称)
注意:关系型数据库中的隐式多对多关系不需要
@relation属性。
消除关系歧义
当您在相同的两个模型之间定义两个关系时,您需要在 @relation 属性中添加 name 参数来消除它们的歧义。例如,考虑以下模型,以说明为什么需要这样做:
- 关系型数据库
- MongoDB
// NOTE: This schema is intentionally incorrect. See below for a working solution.
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
name String?
writtenPosts Post[]
pinnedPost Post?
}
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
title String?
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int
pinnedBy User? @relation(fields: [pinnedById], references: [id])
pinnedById Int?
}
// NOTE: This schema is intentionally incorrect. See below for a working solution.
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
name String?
writtenPosts Post[]
pinnedPost Post?
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
title String?
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId
pinnedBy User? @relation(fields: [pinnedById], references: [id])
pinnedById String? @db.ObjectId
}
在这种情况下,关系是模糊的,有四种不同的解释方式:
User.writtenPosts↔Post.author+Post.authorIdUser.writtenPosts↔Post.pinnedBy+Post.pinnedByIdUser.pinnedPost↔Post.author+Post.authorIdUser.pinnedPost↔Post.pinnedBy+Post.pinnedById
为了消除这些关系的歧义,您需要使用 @relation 属性注解关系字段并提供 name 参数。您可以设置任何 name(空字符串 "" 除外),但它在关系的两侧必须相同。
- 关系型数据库
- MongoDB
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
name String?
writtenPosts Post[] @relation("WrittenPosts")
pinnedPost Post? @relation("PinnedPost")
}
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
title String?
author User @relation("WrittenPosts", fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int
pinnedBy User? @relation("PinnedPost", fields: [pinnedById], references: [id])
pinnedById Int? @unique
}
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
name String?
writtenPosts Post[] @relation("WrittenPosts")
pinnedPost Post? @relation("PinnedPost")
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
title String?
author User @relation("WrittenPosts", fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId
pinnedBy User? @relation("PinnedPost", fields: [pinnedById], references: [id])
pinnedById String? @unique @db.ObjectId
}